Uncertainty has always been part of investing. Every market environment brings its own set of unknowns, which is why a Fidelity portfolio manager recently observed that “uncertainty is the new certainty.”
Judging by the market’s reaction to potential new tariffs involving the EU and Greenland, 2026 is no exception, even if that particular development wasn’t on your bingo card to start the year. This is especially true at a time when the broader economic outlook remains strong in many respects.
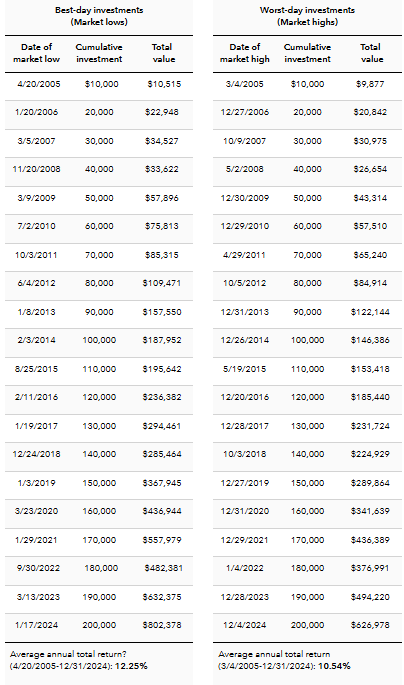
Periods of volatility can be uncomfortable, and some investors respond by selling in haste. We take a different view. Market pullbacks provide opportunities to pick up equities at temporarily reduced prices, and the long-term horizon allows investors to take advantage.
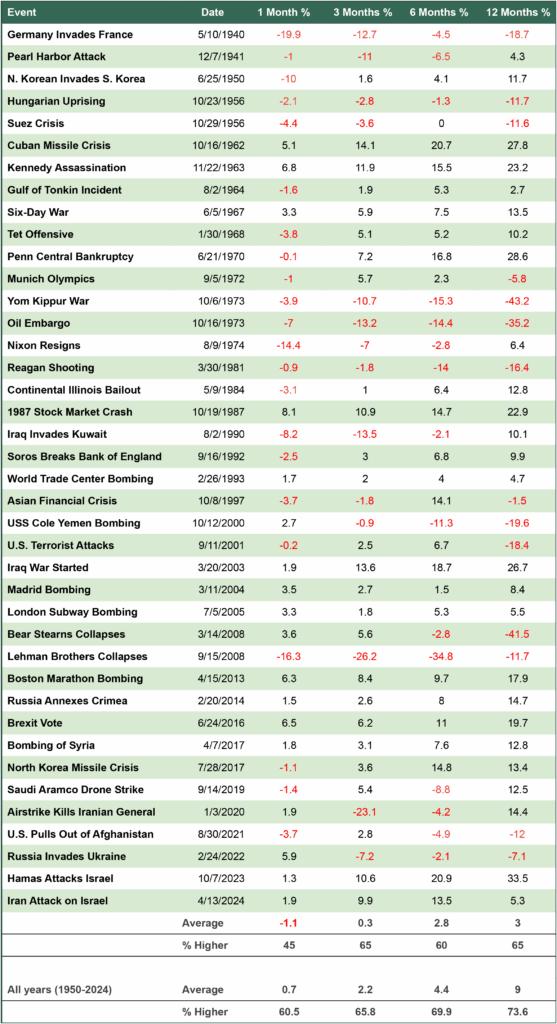
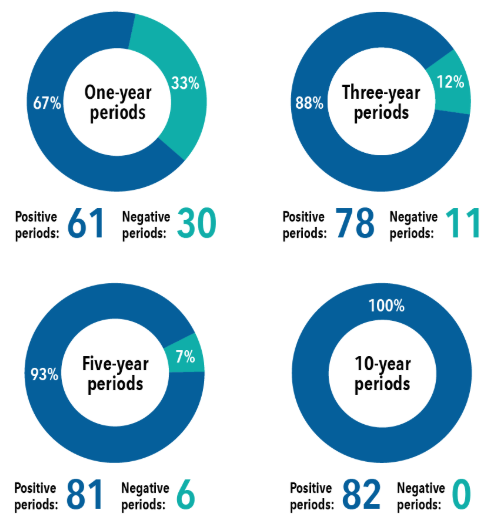
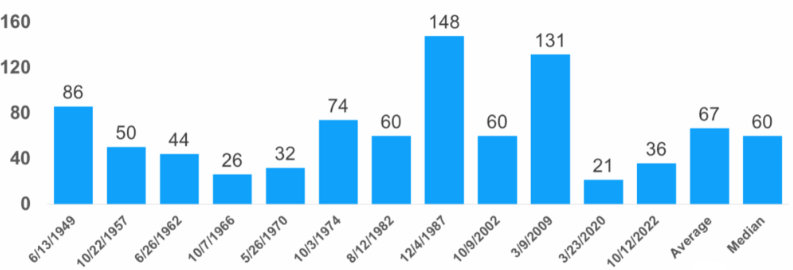
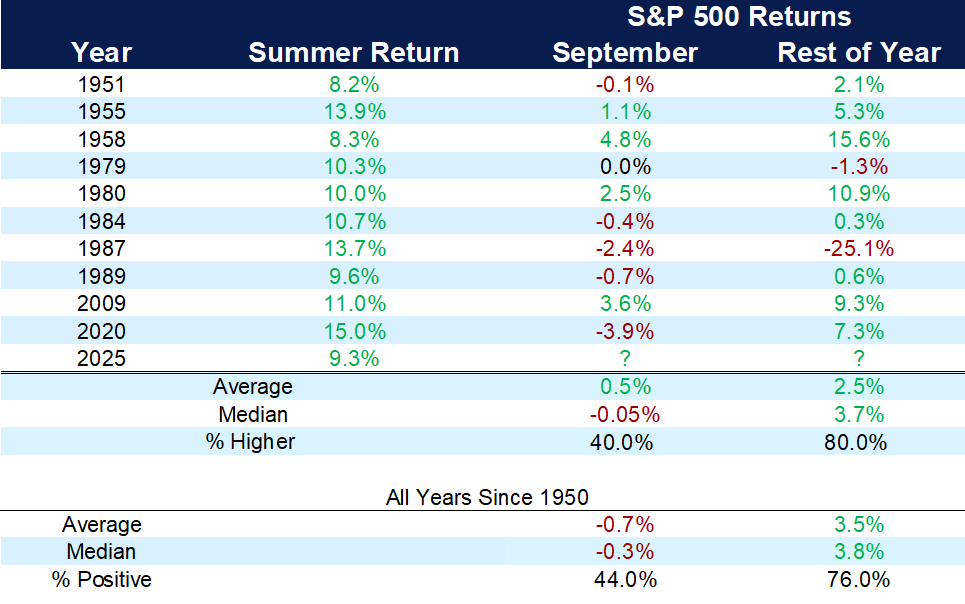
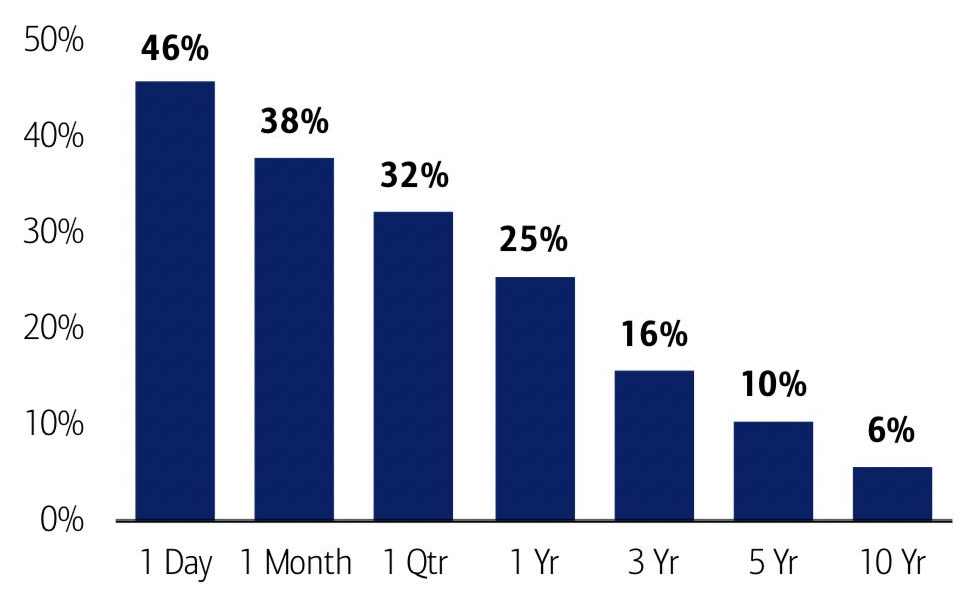
As the chart illustrates, history supports this approach. Since 1929, the probability of experiencing negative returns over a 10-year period has been just 6%. The longer one owns stocks, the lower the likelihood of a loss — declining from 46% over a single day to just 6% over a decade. Time in the market remains one of the most powerful tools investors have.
Time Horizons and Equity Losses
Probability of negative returns based on S&P 500 total returns, 1929-present
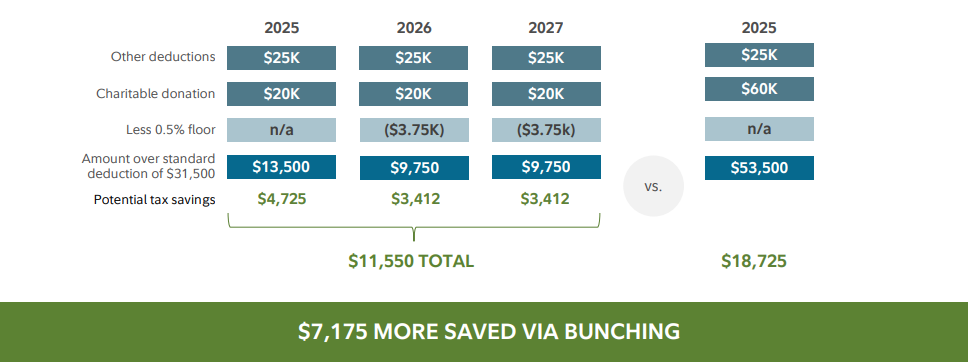
What Many Wealth Firms Avoid Saying Clearly
Long-term investment outcomes are driven far more by client behavior than by market conditions. Many wealth firms hesitate to say this plainly because it can be uncomfortable. But the reality is simple: Clients who stay disciplined and follow their investment team tend to succeed, and those who frequently override strategy tend to undermine results.
Discipline, Not Drama, Builds Wealth
The majority of investors do this right. Most of our clients do. They understand that disciplined, professional portfolio management — not constant reaction to the day’s headlines — is what creates long-term success.
But a small percentage of clients and investors don’t.
• They want to override the process.
• They try to force market timing.
• They react to news, politics, and short-term noise.
And when results suffer, they look for something else to blame. This is where most firms stay silent. We won’t.
Market Timing Is the Fastest Way to Break Compounding
Trying to time the market is not a sophisticated strategy. It’s a gamble that requires two perfect decisions: when to get out and when to get back in.
Very few people make the second decision well. They exit “until things feel better,” watch markets rise, hesitate, then wait for the pullback that never feels safe enough or think that they can’t get back in at a higher level than where they sold.
Meanwhile, compounding keeps moving without them.
Headlines Are Not Signals
Another thing most firms won’t say is that if your portfolio decisions are driven by the news, you’re already late. We hear it constantly:
“Why aren’t we buying this after the announcement?”
“Why didn’t we react when politics shifted?”
“Why aren’t we chasing that story?”
Here’s why: Professional investing does not chase headlines. Markets digest information instantly. Portfolios are built through positioning, not reaction. Acting after the fact adds risk, not insight.
As Wayne Gretzky famously put it, “I skate to where the puck is going to be, not where it has been.” That principle is foundational to how disciplined investing works.
The Vegas Effect: Stories Without Receipts
Here’s another uncomfortable reality: Many people who claim they’re outperforming on their own can never quite produce the full record.
It’s the same phenomenon you see in Las Vegas. Wins get remembered. Losses get discounted. Missed opportunities never make the story. If results were truly consistent and repeatable, transparency wouldn’t be an issue.
The handful of people who can successfully manage their own money over decades does exist, but they’re disciplined, unemotional, process-driven, and rare.
Selectivity Is a Strength, Not a Weakness
Every year, we review our client relationships intentionally — not to judge performance, but to confirm alignment. When a client repeatedly overrides strategy, forces market calls, and then assigns blame for outcomes driven by those decisions, that’s not a market problem.
It’s a fit problem. The discipline required for long-term success wasn’t being followed.
Most firms avoid conversations like this. We don’t. A disciplined investment process only works when it’s allowed to work.
What Actually Works Over Decades
The clients who succeed over the long haul share common traits:
• They stay invested through cycles.
• They allow professionals to manage the portfolio.
• They accept volatility as part of the process.
• They avoid emotional overrides.
That’s how results compound over decades, not months or days.
The Bottom Line
Let’s rip the Band-Aid clean off: Working with wealth management firms and advisors but refusing to follow their guidance defeats the entire purpose.
If you want to build lasting wealth, you don’t need to predict markets. You need discipline. You need consistency. You need to stay in your lane. Most investors who do this succeed, and for the few who won’t, honesty matters more than comfort.
The CD Wealth Formula
We help our clients reach and maintain financial stability by following a specific plan, catered to each client.
Our focus remains on long-term investing with a strategic allocation while maintaining a tactical approach. Our decisions to make changes are calculated and well thought out, looking at where we see the economy heading. We are anticipating and moving to those areas of strength in the economy and in the stock market.
We will continue to focus on the fact that what really matters right now is time in the market, not out of the market. That means staying the course and continuing to invest, even when the markets dip, to take advantage of potential market upturns. We continue to adhere to the proven disciplines of diversification, periodic rebalancing, and forward-looking strategies, while avoiding reliance on stale retrospective data.
It is important to focus on the long-term goal, not on one specific data point or indicator. Long-term fundamentals are what matter. In markets and moments like these, it is essential to stick to the financial plan. Investing is about following a disciplined process over time.
Sources: Bank of America, Fidelity